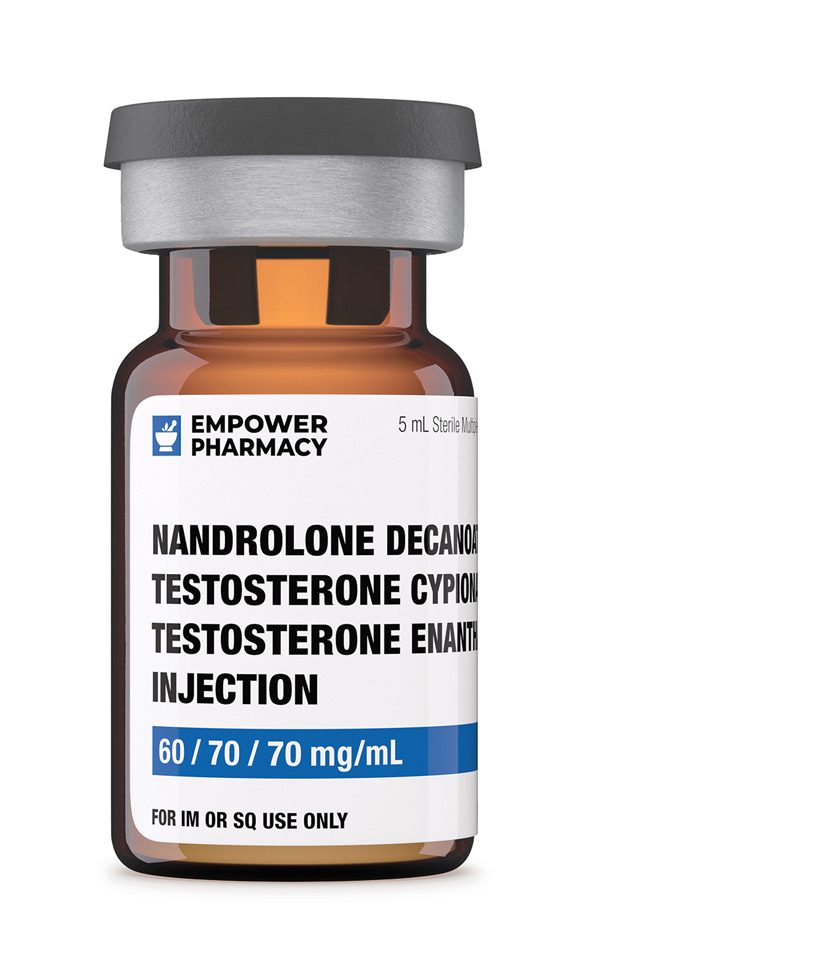
Description
Nandrolone decanoate, also known as 19-nortestosterone, is an injectable medication that belongs to the group of drugs called class II anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS). The drugs that fall under class II AAS are all known as 19-nortestosterone derivatives; they are all synthetic derivatives of the endogenous male hormone testosterone. The primary role of testosterone in the human male is to aid the development of secondary sexual characteristics (androgenic effects) during puberty and the development as well as maintenance of muscle mass (anabolic effects); drugs, such as Nandrolone decanoate, that fall under the AAS category were synthesized to have more anabolic and less androgenic properties.1
Originally synthesized and described by Birch in 1950, nandrolone is similar in chemical composition and structure to testosterone. The only difference in chemical composition between testosterone and nandrolone is that nandrolone lacks a methyl group at carbon C-19. Due to its demethylation at C-19, nandrolone decanoate has very strong anabolic effects but weak androgenic effects; its anabolic effects are much stronger than testosterone.2
One of the main indications for the clinical use of injectable nandrolone decanoate is in the management of refractory anemia that is not responsive to other treatment modalities; nandrolone triggers the production of erythropoietin by the kidneys, which results in an increased red blood cell mass and volume. Additionally, in patients suffering from chronic wasting diseases such as cancer, nandrolone may promote tissue development with the subsequent building of muscle mass. Nandrolone may also be used in the medical management of postmenopausal women who have osteoporosis.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.